- With the proliferation of RFID products, there is a clear understanding of how the technology works and how it works best.
- How does the technology work?
- What is the most effective support depending on its use?
- Which chip to choose?
- To determine your place among the vast selection of media and chips, here are some simple answers SBE answers:
What is RFID?
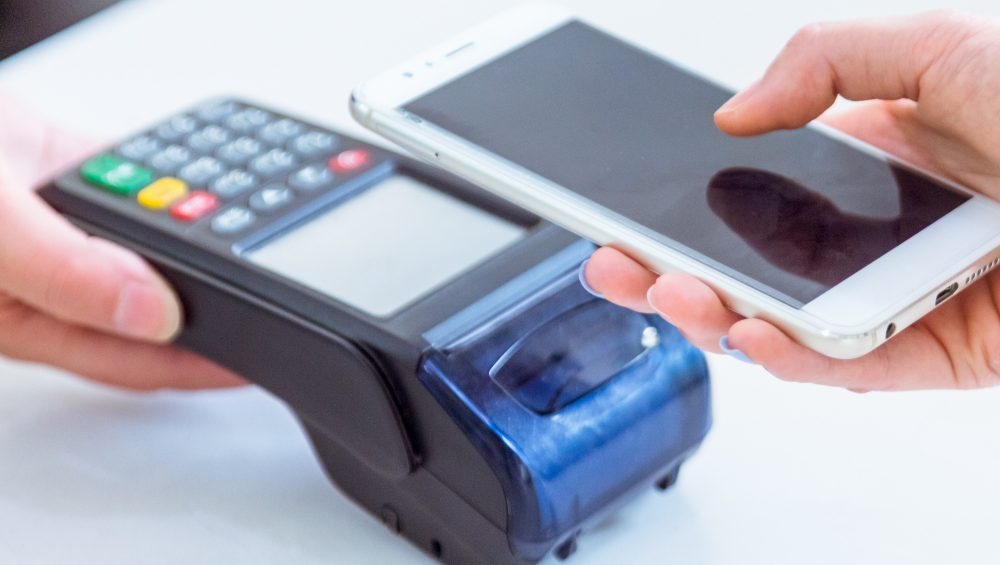
- We use RFID products every day without knowing it: through traffic cards, store locks, RFID badges, badges or, more recently, contactless car keys.
- This technology has the advantage of saving the user time and allowing rapid reading
- But do you really know what RFID is?
- RFID or re-Radio Frequency Identification is a method of storing and retrieving data to
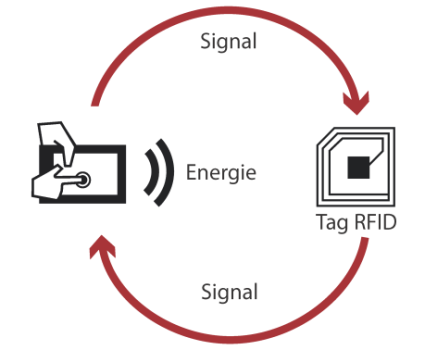
- The system is activated by transmitting electrical energy from a radio tag and RFID transmitter.
- The radio tag is made up of an electronic chip and an antenna, the radio signal emitted by the reader also uses RFID technology.
- Components can both read and respond to signals.
RFID chip or NFC chip?

- NFC stands for near field communication.
- NFC is also based on RFID protocols.
- The main difference with RFID is that a device can act not only as a reader, but also a tag.
- In “peer-to-peer” mode, it is also possible to transfer information between two NFC devices.
- The NFC system operates on the same frequency as the HF RFID system.
- There is therefore only a limited reading range for short distances.
- Due to these limitations, NFC devices must be very close to each other, usually no more than a few centimeters.
- This is why NFC is often used for secure applications, notably for access controls, or used for contactless payments.
- Due to these limitations, NFC devices must be very close to each other, usually no more than a few centimeters.
- This is why NFC is often used for secure applications, notably for access controls, or used for contactless payments.
What frequencies for what reader distances?
- The frequency is the characteristic that establishes the connection between the chip and the antenna.
- So not all chips on the market have the same functionality.
- The chips themselves differ widely in operating mode and reading distance.
- The higher the frequency, the greater the magnetic distance.
- Depending on these factors, the chip will be less powerful and more expensive.
- Several manufacturers share the market and offer more and more efficient ones.
- This technology is now standardized and present in a large part of daily life.
- Discover our 2 RFID readers:
- The UFH RFID reader can quickly read badges, tags and other RFID transmitters indoors and outdoors remotely.
- The USB RFID reader is suitable for rapid contact reading of high and low frequency badges and tags.
The RFID chip, active or passive?
This technology is available in three versions:
- Passive RFID
- Semi-passive RFID
- Active RFID
- Passive RFID operates in read-only mode because there is no battery and the reader must be moved to read it.
- A strong electromagnetic signal is then sent to it, allowing the RFID chip to be activated and read the data it contains.
- On the other hand, RFID works with a source like a small cell or battery, which allows tags to be read at longer distances.
- This technique is mainly used for vehicle traceability or logistics traceability.
- Just like active RFID, semi-passive RFID is powered by a power source.
- However, the battery powers the RFID chip normally.
- This does not send a signal.
- This technology is useful for food traceability, particularly for recording temperature changes during transport.