Production management, definition
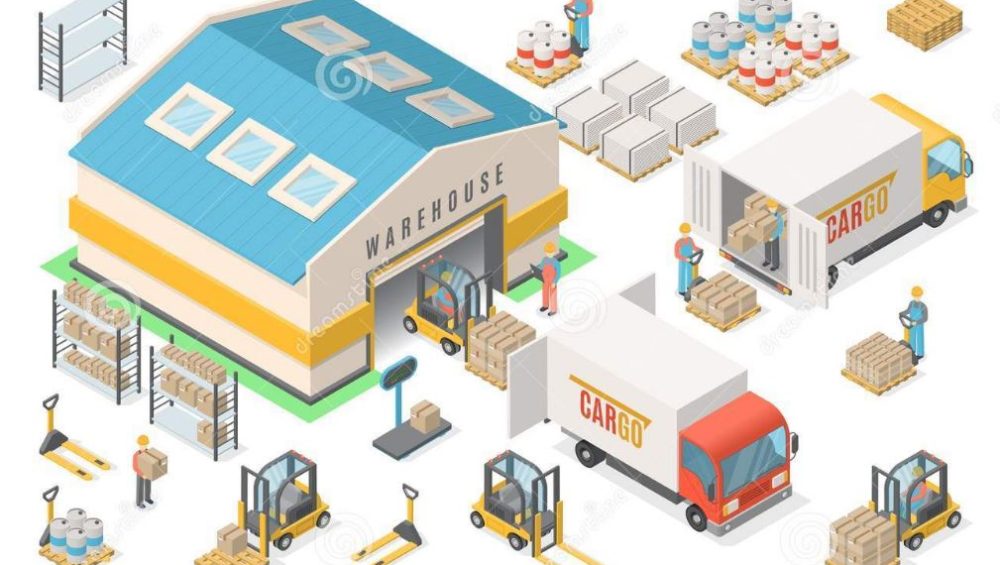
The aim of production management is to organize and rationalize all stages of industrial production. The production cycle is divided into three stages: Planning: generation and distribution of manufacturing orders between machines, production planning. Production: machine operation, operator management and raw material inventory management. Control and recording: quality control, recording of inventory movements, time recording.
The challenges of production management
The quality of production process management is essential to obtain the overall performance of production tools. This is achieved by combining safety and well-being of operators, cost, control of deadlines, quality and respect for the environment. Indeed, the difficulty of production management comes from the simultaneous control of a large number of variables.
Production management software
Computer-aided production management uses digital resources to optimize production management, including planning, real-time monitoring and analysis functions.
The benefits of this solution
The C2M solution improves the synchronization of production processes, the precision and traceability of operations, and improves control of consumption. As a result, production costs of the industrial company were reduced, inventories were limited, lead times were more predictable, productivity increased, production interruptions were reduced and, finally, compliance and quality have improved. Synchronized with business management solutions, or included in an integrated software package, the industry helps streamline and automate the company’s collective operations.
the advantages: Personalization , Technicality , Customer information
Advanced tools further improve performance: calculation of net demand, estimator, planning module… Thus, a rich library of dashboards allows companies to manage the production cycle by defining their own indicators.
Variety of terminology and accuracy of scope contribute to planning, management and control of operations. Indeed, the possibility of modification (subcontracting, component replacement) gives production flexibility and responsiveness.
The traceability of operations and the capitalization of history make it possible to make the information given to customers more reliable. Delivery deadlines are more precise and the ability to keep promises strengthened. Emergency treatment is then made easier.
read more: