Table of Contents
Introduction to E-Commerce
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services online. It involves conducting commercial transactions over the internet, utilizing electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, or tablets. E-commerce has revolutionized the way businesses operate, allowing them to reach a global audience, operate 24/7, and provide customers with convenience and accessibility.
- E-commerce encompasses various types of transactions, including business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), and consumer-to-business (C2B).
- It eliminates geographical limitations, enabling businesses to expand their reach beyond local markets and tap into a global customer base.
- Security measures such as encryption and secure payment gateways have made online transactions safe and reliable, fostering trust between businesses and consumers.
- The convenience of e-commerce allows customers to shop from anywhere at any time, leading to higher satisfaction and increased sales for businesses.
In today’s digital age, e-commerce is a vital component of the global economy, driving sales, facilitating transactions, and shaping consumer behavior. Understanding the fundamentals of e-commerce is crucial for businesses looking to thrive in a competitive online marketplace.
The History and Evolution of E-Commerce
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, has a rich history dating back to the 1960s when businesses started using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to exchange business documents electronically. This early form of e-commerce paved the way for online transactions as we know them today.
- In the 1990s, the internet boom revolutionized e-commerce with the emergence of online marketplaces and retailers. Companies like Amazon and eBay set the stage for the rapid growth of online shopping.
- The early 2000s saw the rise of secure online payment systems and the widespread adoption of e-commerce by consumers. This era marked a significant shift towards convenience and accessibility in retail.
- Mobile commerce, or m-commerce, gained momentum in the 2010s with the increasing popularity of smartphones and mobile apps. Consumers could now shop on-the-go, further boosting the e-commerce industry.
- Today, advancements in technology like artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and voice commerce are shaping the future of e-commerce. Personalized shopping experiences and seamless transactions are becoming the norm.
As e-commerce continues to evolve, businesses must adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological innovations to stay competitive in the digital marketplace. By understanding the history and evolution of e-commerce, companies can better navigate the complexities of online retail and capitalize on emerging trends.

The Benefits of E-Commerce
- Increased Reach: E-commerce allows businesses to expand their reach beyond local customers to a global audience. This can result in increased sales and revenue.
- Convenience: Customers can shop 24/7 from the comfort of their homes, making purchases at any time that suits them. This convenience is a major benefit of e-commerce for both businesses and customers.
- Cost-Effective: Setting up an online store is often more cost-effective than establishing a physical retail presence. E-commerce eliminates the need for expenses such as rent, utilities, and in-store staff.
- Personalization: Online stores can use customer data to offer personalized recommendations and targeted marketing. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased sales.
- Data Insights: E-commerce provides businesses with valuable data on customer behavior and preferences. This data can be used to make informed decisions and tailor offerings to meet customer needs.
- Flexibility: E-commerce allows businesses to quickly adapt to market trends and changes in demand. They can easily update products, pricing, and promotions in real-time.
- Automation: Processes such as order fulfillment, inventory management, and customer service can be automated in e-commerce, saving time and reducing the margin for error.
- Scalability: E-commerce platforms can scale according to business needs. Whether a business is small or large, e-commerce provides the flexibility to grow and expand operations.
- Competitive Advantage: Embracing e-commerce can give businesses a competitive edge in the market by reaching a wider audience, offering better customer experiences, and staying ahead of competitors.
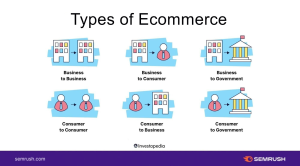
Types of E-Commerce Models
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): In this model, businesses sell products or services directly to consumers. It is the most common type of e-commerce and includes online retail, such as Amazon or Walmart.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses. Companies purchase products or services from other businesses online. Examples include manufacturers buying raw materials from suppliers.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): C2C e-commerce enables consumers to sell products or services to other consumers. It typically occurs through online marketplaces like eBay or Craigslist, where individuals can buy and sell used goods.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): In this model, individuals offer products or services to businesses. Influencers partnering with brands for sponsored content or freelance professionals providing services to companies are examples of C2B e-commerce.
- Business-to-Administration (B2A): B2A e-commerce involves businesses providing products or services to governmental organizations. This model includes companies offering software solutions to government agencies.
- Consumer-to-Administration (C2A): C2A e-commerce refers to individuals accessing government services or information online. This can include paying taxes online or registering for government programs through official websites.
Each e-commerce model caters to specific types of transactions and plays a crucial role in the digital marketplace.
Setting Up Your E-Commerce Business
Starting an e-commerce business involves several key steps to ensure success. Here are essential tips to set up your e-commerce business effectively:
- Choose the Right Platform: Selecting a suitable e-commerce platform, such as Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento, is crucial. Consider factors like ease of use, scalability, and customization options.
- Design Your Website: Create a user-friendly website with a clear layout, easy navigation, and secure payment options. Use high-quality images and compelling product descriptions to attract customers.
- Set Up Payment Gateways: Integrate reliable payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Square to facilitate smooth transactions. Ensure secure payment processing to build trust with your customers.
- Manage Inventory: Implement an inventory management system to track stock levels, update product availability, and manage orders efficiently. Consider dropshipping options to streamline inventory management.
- Optimize for SEO: Improve your website’s visibility on search engines by implementing SEO strategies. Use relevant keywords, optimize product images, and create engaging content to attract organic traffic.
- Establish Customer Support: Provide excellent customer service through multiple channels like live chat, email, and phone support. Address customer queries promptly to enhance their shopping experience.
- Create Marketing Strategies: Develop a solid marketing plan to promote your e-commerce business. Utilize social media, email marketing, influencer partnerships, and SEO to reach a wider audience and drive conversions.
- Monitor Analytics: Track key metrics like website traffic, conversion rates, and customer engagement using tools like Google Analytics. Analyze data to make informed decisions and optimize your e-commerce business.
By following these steps and best practices, you can set up your e-commerce business efficiently and increase your chances of success in the competitive online market.
Understanding E-Commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms are software applications that enable online businesses to manage their website, sales, and operations. Understanding e-commerce platforms is crucial for anyone looking to establish an online store. Here are some key points to consider:
- Features: E-commerce platforms offer a range of features such as product listing, inventory management, payment processing, and order fulfillment. They also provide tools for marketing, analytics, and customer management.
- Types: There are different types of e-commerce platforms, including hosted platforms like Shopify and BigCommerce, open-source platforms like WooCommerce and Magento, and custom-built platforms. Each type has its own advantages and limitations.
- Scalability: A good e-commerce platform should be scalable to accommodate the growth of your business. It should be able to handle an increase in traffic, sales volume, and product listings without compromising performance.
- Mobile responsiveness: With the rise of mobile shopping, it is essential for an e-commerce platform to be mobile-responsive. This means that the website adapts to different screen sizes and devices, providing a seamless shopping experience for customers.
- Security: Security is a critical aspect of e-commerce platforms. They should have robust measures in place to protect customer data, including SSL encryption, PCI compliance, and secure payment gateways.
- Integration: E-commerce platforms should be able to integrate with other software systems such as accounting, CRM, and email marketing tools. This integration streamlines operations and improves efficiency.
- Support: Choose an e-commerce platform that offers reliable customer support. Whether it’s through phone, email, or live chat, having access to responsive support can help resolve issues quickly and minimize downtime.
Understanding these aspects of e-commerce platforms can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right platform for your online store.
E-Commerce Payment Systems
In the realm of e-commerce, payment systems play a vital role in facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers. Here are some key points to understand about e-commerce payment systems:
- E-commerce payment systems are platforms or services that allow online businesses to accept payments from customers electronically.
- These systems provide a secure and convenient way for customers to make purchases online using various payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers.
- One of the most popular e-commerce payment systems is PayPal, which enables users to link their bank accounts or credit cards to make online payments securely.
- Another widely used payment system is Stripe, known for its ease of integration and robust security features, making it a favorite among online businesses.
- E-commerce payment systems often charge a fee per transaction, which can vary based on the provider and the volume of transactions processed.
- Security is a top priority for e-commerce payment systems, with many implementing encryption and fraud detection measures to protect both merchants and customers.
- In recent years, mobile payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay have gained traction, allowing users to make purchases using their smartphones or other mobile devices.
Understanding the different e-commerce payment systems available can help online businesses choose the right solution to meet their specific needs and provide a smooth and secure checkout experience for their customers.
E-Commerce Marketing Strategies
E-commerce businesses thrive on effective marketing strategies to reach and engage with customers in the vast online marketplace. Here are some crucial e-commerce marketing strategies to boost your online presence and drive sales:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Enhance your website’s visibility by optimizing it for search engines. Target relevant keywords, create high-quality content, and improve your site’s authority to rank higher in search results.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Utilize paid advertising on platforms like Google Ads to target specific keywords and demographics. Pay only when users click on your ads, making it a cost-effective way to drive traffic to your site.
- Social Media Marketing: Engage with your audience on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Create compelling content, run targeted ads, and utilize influencer marketing to reach potential customers.
- Email Marketing: Build a strong email list and send out personalized promotions, product recommendations, and updates to keep customers engaged. Automated email campaigns can help nurture leads and drive conversions.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable and relevant content such as blogs, videos, and infographics to attract and educate your target audience. Share this content on your website and across social media channels to build brand authority.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Implement a CRM system to manage customer interactions and analyze data for personalized marketing campaigns. Use customer insights to tailor your messaging and improve retention rates.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure your e-commerce site is mobile-friendly to cater to the growing number of users shopping on smartphones and tablets. Optimize your website for mobile devices to provide a seamless shopping experience.
By incorporating these e-commerce marketing strategies into your online business plan, you can effectively attract, engage, and convert customers in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Managing E-Commerce Operations
- E-commerce operations encompass various aspects that need to be managed effectively to ensure the smooth running of an online business. Here are some key points to consider when managing e-commerce operations:
- Inventory Management:
- Keeping track of inventory levels is crucial to prevent stockouts and maintain customer satisfaction. Utilizing inventory management systems can help streamline this process.
- Order Processing:
- Efficient order processing is essential for timely fulfillment of customer orders. Automating order processing can reduce errors and improve overall efficiency.
- Payment Processing:
- Secure payment processing is a critical component of e-commerce operations. Implementing reliable payment gateways and encryption techniques can safeguard customer financial information.
- Shipping and Fulfillment:
- Choosing the right shipping partners and optimizing fulfillment processes can significantly impact customer satisfaction. Offering various shipping options and providing order tracking can enhance the overall shopping experience.
- Customer Service:
- Providing excellent customer service is key to building customer loyalty. Responding promptly to inquiries, resolving issues efficiently, and offering post-purchase support can help in retaining customers.
- Website Maintenance:
- Regular website maintenance is necessary to ensure that the online platform functions smoothly. Monitoring website performance, updating content, and optimizing for mobile responsiveness are essential tasks.
- Data Security:
- Protecting customer data from cyber threats is paramount in e-commerce operations. Implementing robust security measures, such as SSL certificates and regular security audits, can help mitigate risks.
In conclusion, effective management of e-commerce operations is essential for the success of an online business. By addressing key areas such as inventory, order processing, payment processing, shipping, customer service, website maintenance, and data security, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and deliver a seamless shopping experience to customers.
E-Commerce Security and Privacy
E-commerce security and privacy are critical aspects of online shopping that both consumers and businesses must prioritize. Here are some key points to consider:
- Secure Payment Methods: Utilize secure payment gateways that encrypt customer data to prevent fraud and protect sensitive information.
- SSL Certificates: Websites should have SSL certificates to ensure secure connections and data encryption, especially during payment transactions.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Implement two-factor authentication for an added layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity through an additional step.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities, address potential threats, and maintain the highest level of protection.
- Privacy Policies: Clearly outline privacy policies to inform customers about how their data will be used, stored, and protected.
- GDPR Compliance: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to safeguard customer data and enhance trust.
- Strong Password Policies: Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords and regularly update them to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive information such as customer details, payment data, and login credentials to prevent unauthorized access and protect data integrity.
In the realm of e-commerce, security and privacy should be paramount to build trust with consumers and safeguard sensitive information from cyber threats and breaches.
Advantages of e-commerce
- Global Reach: E-commerce allows businesses to reach a global audience, breaking down geographical barriers and expanding market reach.
- Cost-Effective: Setting up an online store is often more cost-effective than establishing a physical storefront, saving on rent, utilities, and other expenses.
- Convenience: Customers can shop 24/7, from anywhere with an internet connection, providing convenience and flexibility.
- Increased Sales: E-commerce enables businesses to reach a larger customer base, leading to increased sales and revenue potential.
- Personalized Marketing: E-commerce platforms can track customer behavior and preferences, allowing for personalized marketing strategies.
- Data Analysis: Businesses can collect and analyze customer data to make informed decisions and tailor offerings to customer needs.
- Efficiency: E-commerce streamlines the buying process for both businesses and customers, reducing the time and resources required for transactions.
- Scalability: Online stores can easily scale operations to accommodate growth without the constraints of physical space.
- Access to New Markets: E-commerce opens up opportunities to target niche markets and explore new customer segments.
- Competitive Advantage: Embracing e-commerce can give businesses a competitive edge by offering a modern, convenient shopping experience.
Incorporating e-commerce into business operations can provide numerous advantages that contribute to growth, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages of E-commerce
- E-commerce platforms are prone to technical issues, such as website crashes, which can lead to a loss of sales and damage to the business’s reputation.
- There is a lack of personal interaction in e-commerce, which can make it challenging to build trust with customers and provide personalized assistance.
- Cybersecurity threats, such as data breaches and hacking, are significant concerns for e-commerce businesses, as they deal with sensitive customer information.
- E-commerce businesses face intense competition, as barriers to entry are relatively low, leading to price wars and margin pressures.
- Logistics and shipping costs can be high for e-commerce businesses, especially if they operate on a global scale, impacting profit margins.
- Returns and refunds processes can be complex and costly for e-commerce businesses to manage, affecting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
“Despite the numerous advantages of e-commerce, businesses must also navigate through these challenges to ensure sustainable success in the online marketplace.”
E-commerce Applications
E-commerce applications cover a wide range of digital platforms and tools that enable online transactions between businesses and consumers. Here are some key aspects of e-commerce applications:
- Online Stores: E-commerce applications power online stores where businesses can showcase and sell their products or services to customers around the globe. These platforms often include features like product listings, shopping carts, and secure payment gateways.
- Mobile Commerce: With the rise of smartphones, e-commerce applications have expanded to encompass mobile commerce. Mobile apps and responsive websites allow customers to browse and make purchases conveniently from their mobile devices.
- Digital Wallets: E-commerce applications often integrate digital wallet services, allowing customers to store their payment information securely for quick and easy transactions. Popular digital wallet providers include PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay.
- Subscription Services: Many e-commerce applications support subscription-based models, where customers can sign up for recurring deliveries of products or access to digital content. This model provides businesses with a consistent revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty.
- Marketplace Platforms: E-commerce applications also power online marketplaces where multiple sellers can list their products for sale. Examples of marketplace platforms include Amazon, eBay, and Etsy, which connect sellers with a vast customer base.
- Personalization and Recommendation Engines: Advanced e-commerce applications leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to personalize the shopping experience for customers. These systems analyze customer data and behavior to offer tailored product recommendations and promotions.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): E-commerce applications often include CRM functionality to help businesses manage interactions with customers, track sales, and provide responsive customer support. CRM systems help businesses build long-term relationships with their customer base.
- Analytics and Reporting: E-commerce applications provide detailed analytics and reporting tools that allow businesses to track key metrics like sales performance, customer demographics, and marketing ROI. These insights help businesses make data-driven decisions to optimize their e-commerce operations.
E-commerce platforms and vendors
- E-commerce platforms are online software tools that enable businesses to build and manage their online stores. These platforms provide features such as website design, product catalog management, payment processing, and order fulfillment.
- Some popular e-commerce platforms include Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, and Magento. Each platform has its own features, pricing structure, and target audience, so businesses should choose the one that best fits their needs.
- Vendors, also known as online retailers or e-tailers, are businesses that sell products or services online. They can operate their own e-commerce website or sell through online marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, or Etsy.
- Vendors are responsible for sourcing products, managing inventory, processing orders, and providing customer support. They can be small businesses, large corporations, or individuals selling products as a side hustle.
- E-commerce platforms and vendors work together to create a seamless online shopping experience for customers. Vendors use e-commerce platforms to set up and run their online stores, while customers visit these stores to browse products, make purchases, and track their orders.
- Together, e-commerce platforms and vendors have revolutionized the way people shop, making it easier and more convenient to buy products and services online from the comfort of their homes.
Government Regulations for E-Commerce
- E-commerce businesses must adhere to various government regulations to operate legally and ethically. These regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and promote the overall trustworthiness of online transactions.
- Data Protection: E-commerce businesses are often required to comply with data protection laws to safeguard customer information. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe mandate stringent measures for data collection, storage, and usage.
- Consumer Protection: Governments enforce consumer protection laws to safeguard the rights of online shoppers. Regulations cover aspects such as accurate product descriptions, transparent pricing, timely delivery, and a fair return policy.
- Online Payments: Regulations related to online payments focus on ensuring secure transactions and protecting sensitive financial information. E-commerce businesses must comply with standards like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Taxation: Tax laws for e-commerce can be complex due to the borderless nature of online sales. Businesses may be subject to different tax obligations based on factors like the location of customers, the type of products sold, and the company’s physical presence.
- Advertising Standards: Governments regulate online advertising to prevent misleading or deceptive practices. E-commerce businesses must ensure that their marketing content is truthful, not misleading, and compliant with advertising standards.
Disruption to physical retail (From : “techtarget.com“)
Given the increase in e-commerce use in recent years, analysts, economists and consumers have debated whether the online B2C market will make physical, brick-and-mortar stores obsolete. There’s little question that online shopping is growing at a significant rate. Gartner’s 2023 “Magic Quadrant for Digital Commerce” estimated that by 2025, 80% of B2B sales transactions between suppliers and buyers will take place in digital spaces or channels.
Data from the U.S. Census Bureau shows the increasing importance of e-commerce in the U.S. retail market. The percent of total U.S. sales from e-commerce has consistently grown since 1999.
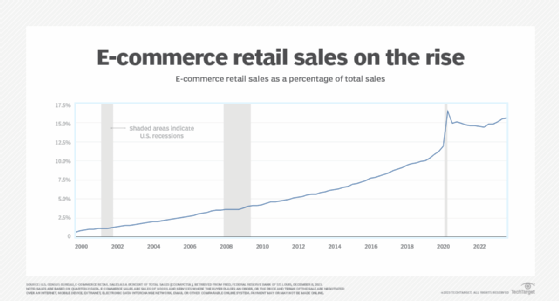
Despite the growth of online retail, many shoppers still prefer brick-and-mortar storefronts. In a 2023 report, Forrester analysts predicted that most retail sales will continue to come from physical stores and traditional retail. They estimated offline sales in the U.S. will reach $4.2 trillion and account for 72% of the country’s retail sales by 2028.
Adoption of new tech also plays a part in the growth of online retail. A 2021 study from Juniper Research predicted e-commerce transactions made using a voice assistant will grow more than 320% to $19.4 billion by 2023 from $4.6 billion in 2021.
A consistent example of the effect e-commerce growth has had on physical retail is the post-Thanksgiving Black Friday and Cyber Monday shopping days in the United States. According to the National Retail Foundation’s 2023 Thanksgiving Weekend Consumer Survey, about 90.6 million consumers made online purchases on Black Friday, up from 87.2 million in 2022. On Cyber Monday, approximately 73 million consumers shopped online.
M-commerce is one of the most important reasons why businesses should consider building mobile apps to better reach and engage with customers. Learn seven potential benefits for businesses gain from going m-commerce.
In conclusion, understanding and complying with government regulations is crucial for the success and longevity of an e-commerce business. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in legal consequences, financial penalties, and damage to the reputation of the business. By staying informed about relevant laws and proactively ensuring compliance, e-commerce businesses can build trust with customers and foster a secure online shopping environment.